
You may have heard of inulin and its health benefits but perhaps you’re not quite sure exactly what is inulin?
What is inulin?
Inulin is a type of soluble fibre and a sugar; a Fructan. Fructans are a series of fructose molecules that are linked together and cannot be broken down in the small intestine.
As a fibre that is not digested by the body, it is a fermentable prebiotic fibre and therefore recommended for a healthy microbiome, as a food source for the good bacteria in the gut, specifically the bowel lower down in the gut.
Food-wise, what is inulin found in? You’ll find Inulin naturally in many foods that you are likely eating already, including:
- Bananas
- Leeks
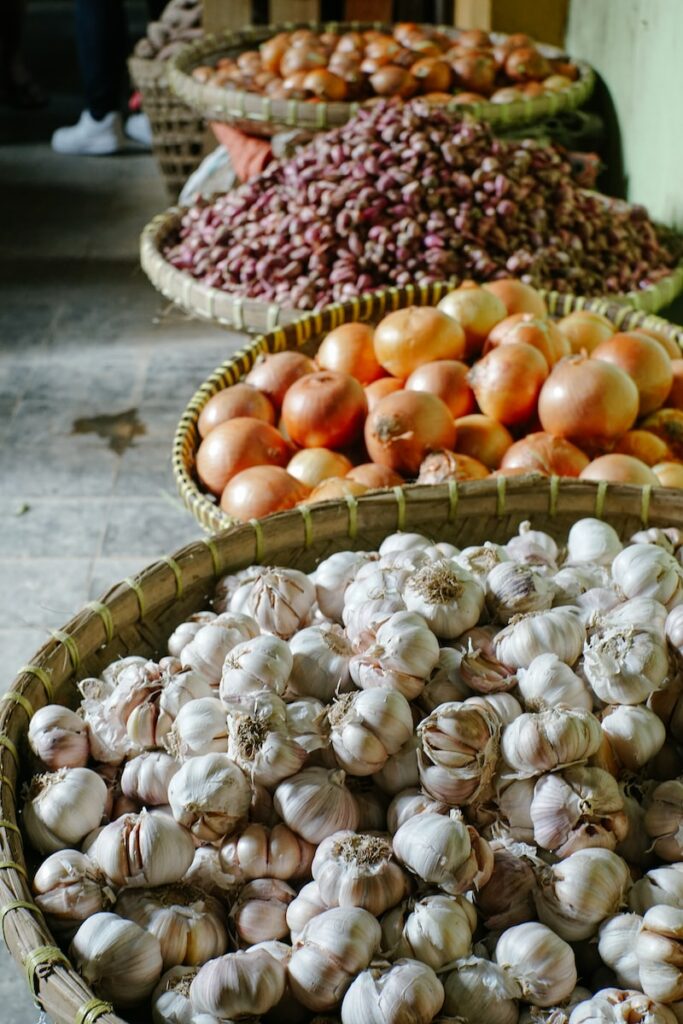
- Onions
- Garlic
- Oats
- Jerusalem Artichokes
- Asparagus
- Wheat
- Chicory root
It is found naturally in many foods and often extracted from chicory root and added to processed foods as a sweetener to replace sugar in foods or a fat substitute in fat-free or reduced-fat foods. Many protein/cereal bars, yoghurts, drinks, baked foods and desserts will contain inulin in supplement form.
It can have some health benefits, some less researched than others.
What is inulin good for?
Digestive Health
Good gut health is dependent on the right balance of good vs bad bacteria. As a prebiotic, inulin acts as food for the good bacteria in the gut, allowing them to thrive and proliferate, and consequently decreasing the harmful bacteria. A meta-analysis published in the European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases noted this consistent effect across the 9 studies evaluated.
Bowel Movements
As a dietary fibre, it can help to stimulate bowel movements, preventing or relieving constipation and improving the consistency of loose stools. Ensuring adequate hydration is also key here.
Weight Management
As a soluble fibre, inulin will combine with water to create a gel consistency, which can mean your stomach empties more slowly, allowing you to feel satiated for longer. It can therefore mean less consumption of unhealthy foods, that are high in calories which over the long term can help with weight management. Whilst participants in trials did report feeling fuller for longer as well as reduced cravings, these positive outcomes were inconsistent and some effects were only noted at the outset whilst others found no significant effects at all.
Blood Sugar Control
Unlike other starchy carbohydrates, inulin does not increase your blood sugar. This is because it is indigestible and not broken down in the stomach.
Indeed, since inulin is a fibre, any supplementation, either by eating inulin-containing foods or with a functional food supplement, will slow down digestion and therefore also slow down the release of sugars into the blood, reducing the risk of blood sugar surges.
This will also help with weight management as insulin release to manage blood sugars is more regulated. Insulin is a fat-storing hormone; high levels of insulin will result in weight gain.
What do you need to look out for?
As inulin is high in fibre, whether in food form or as a supplement, it can cause gastrointestinal side effects and sometimes these effects can be extreme. Diarrhoea and even urgency are common, as well as bloating, flatulence and cramps.
Gradually increasing consumption and staying hydrated will help but extra attention should be considered before beginning inulin supplementation. Do not ignore severe symptoms that are painful and uncomfortable.
The bottom line
A healthy microbiome is fundamental to overall health and inulin plays an important role in increasing the good bacteria in the gut and preventing the development of inflammatory bowel disease. Including inulin-containing foods regularly in the diet will also regulate blood sugars, reducing the risk of insulin resistance and potentially developing type 2 diabetes.
However, research is limited and inconclusive when it comes to the actual benefits and effects of inulin supplementation within the body.
FOOD FIRST! As inulin is found in many foods, eating foods containing inulin is ideal to ensure you consume adequate amounts without incurring any uncomfortable side effects. Eating these foods will offer health benefits as discussed above and should be included regularly in food choices as part of a healthy balanced diet. A fibre-rich diet is crucial for good health.
Look out for inulin supplement weight loss claims. As discussed, inulin can help to balance blood sugars and help you to feel fuller for longer, both helping with weight loss. However, consuming it in larger quantities for this sole purpose will likely lead to severe digestive symptoms. It is important to consume inulin-containing foods, which will support your digestive health and weight loss efforts more naturally and with less harsh effects.
If you do consider supplementation, it is important to start with a minimal dose and build up as necessary over a few weeks. I do not recommend self-prescribing without consulting with a health professional beforehand.








0 Comments